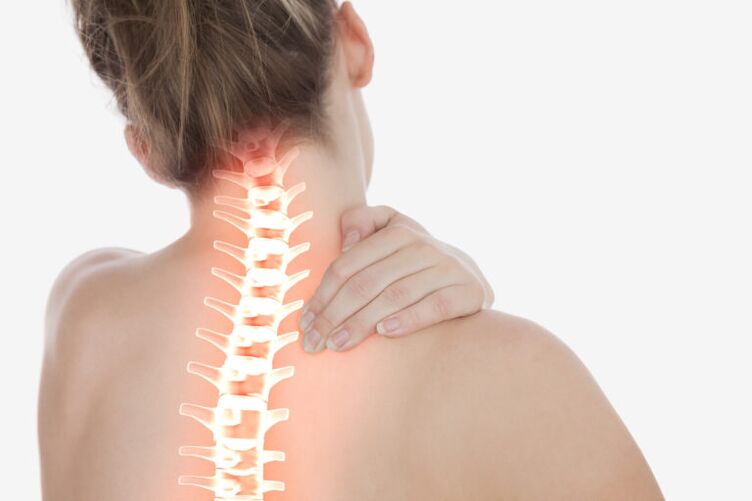
Cervical osteochondrosis, or osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, is a common disease of knowledge workers. Rapidly progressing disease. Cervical osteochondrosis, complicated by the development of disc hernias, is associated with an increase in the incidence of early strokes. An MRI scan is required for diagnosis.
What is cervical osteochondrosis?
Cervical osteochondrosis is a common cause of neck pain, headache, pressure surges, shoulder pain, numbness in the fingers, pain under the shoulder blade. Currently, the incidence of cervical osteochondrosis has increased significantly as the role of the computer in our lives has grown.
However, a fall or injury can make osteochondrosis more likely, and disc degeneration (wear and tear) over time can lead to symptoms.
Symptoms
In addition to moderate or mild pain, a feeling of stiffness in the neck, and in some cases restricted mobility, many patients with cervical osteochondrosis experience numbness, tingling, and even weakness in the neck, arm, or shoulder from chemicals, irritation and pinched nerves in the cervical spine.
For example, pinching a nerve root on the C6-C7 segment can lead to weakness of the triceps, shoulder or forearm muscles, weakness of the wrist muscles, "hanging" of the hand and a change in sensitivity of the middle finger.
Cervical osteochondrosis also often leads to the development of stenosis (narrowing) of the spinal canal and other progressive diseases, such as: B. a herniated disc. How does this happen?
Osteochondrosis is nothing more than a degeneration of the vertebral structures, usually caused by the natural aging of the body. With age, there is a thickening of the ligaments, the formation of bone growths on the vertebrae and other changes. When the spinal ligaments thicken or bone growth occurs, as well as for a number of other reasons, there is less room for the spinal cord and nerves in the spinal canal. This condition is known as stenosis; H. Narrowing of the spinal canal. A severe narrowing of the spinal canal can lead to compression of the nerve roots or even the spinal cord itself.
In most cases, a herniated disc is also a consequence of degeneration. Intervertebral discs act as shock absorbers for the friction between the vertebrae and thus prevent their destruction. Over time, the intervertebral disc loses moisture and nutrients, becomes flatter, more fragile and less elastic. This can cause a tear to form in the annulus, through which part of the nucleus pulposus is pushed out into the spinal canal. This condition is known as an intervertebral hernia. If a herniated disc compresses a nearby nerve root, pain syndrome and / or corresponding neurological symptoms occur.
diagnosis
Successful diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis begins with a medical consultation. The doctor will write the patient's medical history and perform a physical exam to check the mobility and sensitivity of the neck. During the examination, the patient may be asked to make certain movements and to report how the pain symptoms are changing (increasing or decreasing).
If the exam suggests that more tests are needed, your doctor may recommend x-rays such as radiography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT). These diagnostic tests can confirm the presence and location of osteochondrosis with varying degrees of reliability, as well as identify other conditions (e. g. , calcification or arthritis) that may be causing the patient's symptoms.
The best option for X-ray examinations is currently MRI, because with the help of a magnetic resonance tomograph it is possible to obtain high-quality detailed images not only of bone tissue, as in radiography, but also of soft tissues of the spine, including muscles, ligaments, vessels, nerves and intervertebral discsobtain. A CT is usually prescribed when there are contraindications to MRI, the most important of which is the presence of metal structures or devices in the body (artificial joints, pacemakers, etc. ). The quality of CT scans is lower than that of MRI scans, but they can also reveal the condition of the soft tissues of the spine.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
Conservative (without surgery) treatment of osteochondrosis is always recommended as the primary strategy, and surgery is only considered if complex conservative treatment has been unsuccessful for at least six months, or if pain and other symptoms significantly interfere with the patient's daily routine.
Methods used in conservative treatment of cervical osteochondrosis can include:
- Train the spine (train). The stress-free methods of spinal traction used recently make it possible to completely eliminate the complications of this method of treatment, without which traction with stress cannot do. With an increase in the intervertebral disc spacing, the nutrition of all intervertebral discs improves and the pain syndrome disappears.
- Remedial gymnastics. . Remedial gymnastics can improve the mobility of the spine segment. In the moving vertebral segment, no hernias or bulges grow or form because the intervertebral discs fulfill their function.
- massotherapy.
- Drug therapy. Includes NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) and pain relievers. In most cases, drug therapy has little or no temporary effect.
- cervical corsets, orthopedic pillows. They can be recommended to stabilize the cervical spine and reduce pressure on the nerve root after trauma and spinal fractures.
Surgical treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
If there is no significant relief after six months of conservative treatment and the patient's daily routine becomes difficult, surgery may be considered. Typically, for cervical osteochondrosis, a procedure called spinal fusion is performed to immobilize the affected vertebral segment. During this operation, the intervertebral disc is removed, the nerve root decompressed, and a bone or metal implant is used to maintain or create a normal disc space and to stabilize the spinal segment.
As a rule, the spine stiffening is performed on one vertebral segment, in rare cases the question of an operation on two vertebral segments can also be considered. However, the patient needs to know that surgery to relieve neck pain is less likely to produce positive results than similar surgery to relieve pain in the arm for cervical osteochondrosis. Therefore, when neck pain is the main or only symptom, spinal fusion should only be recommended as a last resort or when all conservative treatments have been tried and failed. If the disc space cannot be identified as the most likely cause of neck pain, it is best to avoid surgery, even if conservative treatment does not provide significant pain relief. In addition, do not forget that spinal surgery can be associated with quite serious consequences both in the operated area (local infection, implant rejection, etc. ) and for the whole body (blood clots, allergic reactions to drugs, etc. ). ). Therefore, before deciding on any surgical treatment, you need to discuss all the details of the operation directly with the surgeon who will perform it. It should also be noted that surgery on the cervical spine most often results in a spinal obstruction for the patient.
What is cervical osteochondrosis?
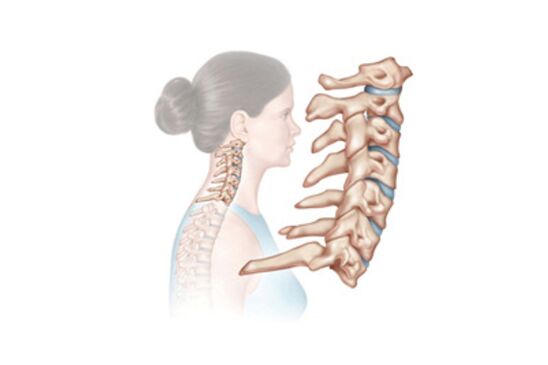
Official medicine interprets osteochondrosis as a degenerative-dystrophic lesion of the intervertebral discs.
From which part of the spine these intervertebral discs are located, the definition of the disease is also given.
Let us specifically consider the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis, which makes up almost 80% of all diseases of our back.
The sad factor is that the disease affects the category of patients aged 30 to 50, that is, in the prime of their ability to work.
In young people, the disease acts as an independent ailment, in old age it is already a pathology that has developed against the background of other joint diseases.
How is the disease developing?
For each part of the spine, a phased development of the disease is characteristic. Cervical osteochondrosis does not go beyond this framework, so it is worth going into detail about each of its stages.
- In the initial stage, the intervertebral discs are gradually destroyed. Between them there is an annulus fibrosus, in which cracks appear, which lead to a decrease in the elasticity and strength of the intervertebral discs themselves. They shrink and compress the nerve roots.
- The second stage is a consequence of the untreated first stage. The incipient destruction of the intervertebral discs turns into a chronic form, tissue compression occurs, and contortions of the cervical vertebrae are observed. Falling head syndrome often develops at this stage.
- At the third stage, the sensations of pain intensify, there is a constant headache, the sensitivity of the upper limbs is lost, and the cervical vertebra is tormented. This is because the fiber ring is almost completely destroyed at this stage.
Often there is a decrease in pain sensation of third degree cervical osteochondrosis. This happens the moment the cartilage tissue disappears and there is nothing to hurt.

causes
Given the prevalence of osteochondrosis in general, doctors began to carefully examine its causes. Many of the negative factors have been identified, but there is no definitive list. Here are the ones announced so far:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- all kinds of poisoning and infections;
- great physical activity;
- Smoking;
- constant weightlifting;
- Stress and nervous tension;
- uncomfortable shoes or an irregular foot that puts unnecessary pressure on the spine;
- wrong diet;
- frequent hypothermia and exposure to bad weather;
- age-related changes;
- Spinal injury;
- bad inheritance;
- a sharp refusal to exercise if they have done so long before.
After familiarizing yourself with the reasons, it becomes clear that cervical osteochondrosis can occur at any age. And if the symptoms of osteochondrosis are insignificant at the beginning and are characterized by rare attacks of pain, then over time it turns out that it is also impossible to turn your neck and tilt your head with difficulty. And those aren't the only dangers of the disease.
What is the danger of the disease
Our throat is a great worker. She is involved all day, and her little eddies stoically withstand all our twists and turns of the head. When the bones are displaced, nerves are pinched and blood vessels compressed and the vertebral artery, which is responsible for nourishing the brain, also crosses the cervical spine. The artery is compressed, the nerve root is compressed, and the inflammatory process begins.

What does this lead to? Spinal stroke, ischemia, intervertebral hernia - these are the serious consequences of cervical osteochondrosis. We add here a general decrease in motility and the formation of osteophytes. As a result, we have a disability that threatens complete immobility. With such a disappointing prognosis, it is important to identify the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis quickly.
Symptoms

The shortest way to recognize osteochondrosis is through the patient's complaints. What feelings does a person speak of when his cervical vertebrae are destroyed? The clinical picture looks like this:
- Dizziness;
- Strong headache;
- "Flies" and colored spots in the eyes on the background of pain in the head;
- pain when turning, lifting weights;
- Pain that radiates to other organs (heart region, other organs).
Sometimes signs of osteochondrosis can be counted among other diseases, but even if they are temporary, they cannot be ignored.
Diagnosis and treatment
Continuing with the feelings expressed by the patient, the neurologist proceeds to a more accurate diagnosis of the disease. A few years ago, doctors only had x-rays in their arsenal to detect osteochondrosis. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are actively used today. They allow you to accurately determine the stage of the disease.
After evaluating the resulting image, a specialized vertebroneurologist will prescribe the necessary treatment. The first thing the doctor takes is to relieve pain, then swelling and inflammation. Such anti-inflammatory drugs are used to relieve pain. As we will recall, the compression of the vertebral artery disrupts supply to the brain and therefore needs to be improved. This is done with the help of muscle relaxants.

Knowing that the symptoms and treatment of cervical osteochondrosis affect the spine, massage and physiotherapy exercises necessarily belong in the complex of health-promoting measures. The massage is carried out by a specialist and by the patient himself. There are also special exercises that aim to develop the cervical vertebrae and restore their mobility.





















